
- #Ubuntu ftp server install install
- #Ubuntu ftp server install upgrade
- #Ubuntu ftp server install windows
So far you are ready to use ftpuser to connect and login to your new FTP server. If you want to use FTP on any other network than your local network, then it is better to configure SFTP server to add security to your FTP connections.
#Ubuntu ftp server install install
Install Vsftpd to configure FTP server to transfer files.
#Ubuntu ftp server install windows
Now your FTP server configuration is over. CentOS Stream 9 CentOS Stream 8 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Windows Server 2022. $ sudo bash -c “echo FTP TESTING > /home/ftpuser/FTP-TEST”
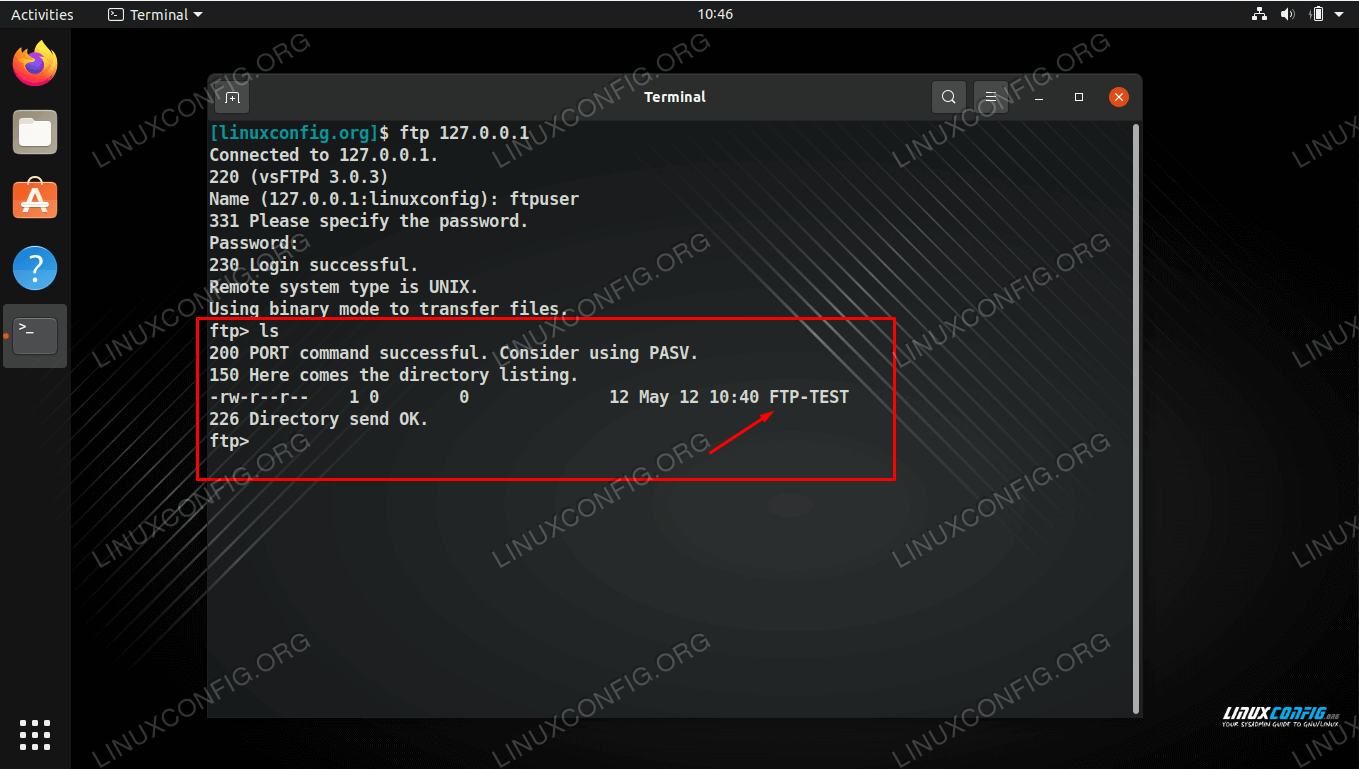
If you log in you can able to see and edit this file. To test it create an arbitrary file within ftpuser ‘s home directory. If you want to create a new system account i.e. Now you have to restart VSFTPD server to apply new changes. $ sudo ufw allow from any to any port 20,21,10000:10100 proto tcp This screen selects the language for the installer and the default language for the installed system. However, this reference guide provides more information for each of the screens of the installer. If your UFW firewall is enabled then execute the below command to allow traffic to FTP ports. The installer is designed to be easy to use without the need to refer to documentation. Rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.keyĪdd this FTP configuration lines to /etc/nf file. Rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem Now you have to start basic FTP server configuration, and make sure that it is working and after assuring that it suited to all environments. Change settings: Now we will need to change the necessary settings in the vsftpd configuration file.
#Ubuntu ftp server install upgrade
Login into your server using SSH and upgrade it: 2. Now you have to create a new configuration file /etc/nf using text editor as shown below VPS with Ubuntu 14.04 or 16.04 operating system installed. Next step is to configure the VSFTPD.īefore configuring FSFTPD server, you have to take a backup for current server configuration file: To do this you have to open the terminal and enter the below command. Whats up Linux Community In this video, I walk through the install and configuration of an FTP server (vsftpd) on Ubuntu 20.04. Create a non-root user account with sudo privileges by following our guide, (.įirst of all, you have to install VSFTPD Thread. Privileged access to the system as root or a non-root user account with sudo privileges is required.
It is built on a client-server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and server. ( is a standard network protocol used for transfer of computer files between a client and server on Computer network. Not to worry! Create a new directory for the user receiving the error ( user2 in this case) that is a subdirectory of their home directory ( /home/user2).– (#vsftpd-installation With certain version of vsftpd you may receive the following error: 500 OOPS: vsftpd: refusing to run with writable root inside chroot(). Service vsftpd restart Step 3: Configure the User’s Home Directory Local users will be ‘chroot jailed’ and they will be denied access to any other part of the server change the chroot_local_user setting to YES:Įxit and save the file with the command :wq. If you want local user to be able to write to a directory, then change the write_enable setting to YES: Let’s edit the configuration file for vsftpd:ĭisallow anonymous, unidentified users to access files via FTP change the anonymous_enable setting to NO:Īllow local uses to login by changing the local_enable setting to YES: Then let’s install vsftpd and any required packages:Īpt-get -y install vsftpd Step 2: Configure vsftpdįor a refresher on editing files with vim see: New User Tutorial: Overview of the Vim Text Editor Consider securing your FTP connection with SSL/TLS.įirst, you’ll follow a simple best practice: ensuring the list of available packages is up to date before installing anything new. Warning: FTP data is insecure traffic is not encrypted, and all transmissions are clear text (including usernames, passwords, commands, and data).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
